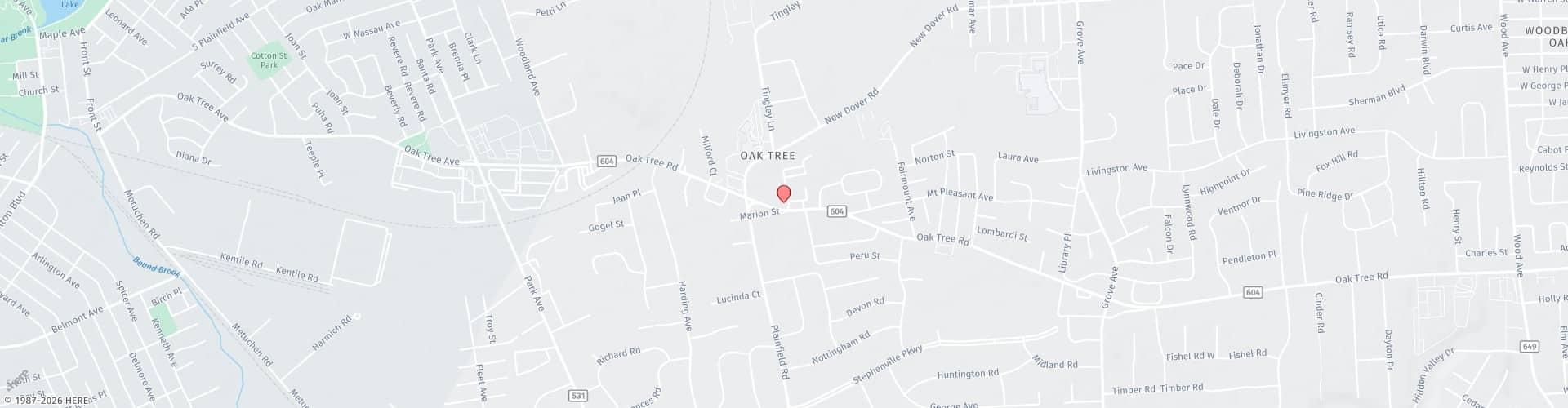
Gum disease is one of the most common oral health concerns adults face, and treating it requires skill and experience. Gentle Dental Care provides advanced treatment options. Our dentists have extensive training in general and cosmetic dentistry services, with additional expertise in managing periodontal issues from early gum inflammation to advanced tissue damage.
We’re focused on your long-term oral health, not quick fixes. Whether managing early signs of gum disease or performing more advanced procedures, our goal is to restore your dental health in a way that’s comfortable and sustainable. We welcome patients seeking skilled treatment for gum disease and other dental concerns in Edison, New Jersey.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is a chronic infection that affects the gums and the structures supporting your teeth. It starts when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—builds up along the gumline. If not removed through brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, plaque hardens into tartar, which allows bacteria to spread below the gumline.
As bacteria grow, they irritate and inflame the gum tissue. This early stage is called gingivitis, which often causes redness, swelling, and bleeding, especially during brushing. Without treatment, the infection progresses deeper. The gums begin to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where more bacteria can collect. This leads to further breakdown of the bone and tissue that hold your teeth in place.
In advanced stages, periodontal disease weakens the jawbone and connective tissues. Teeth that once felt stable can loosen or fall out. Left untreated, periodontal disease is a major cause of adult tooth loss. Early care is key to stopping this process and protecting both your gums and your overall health.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
The primary cause of periodontal disease is the buildup of plaque. However, other factors can play a role, such as:
- Buildup of plaque (primary cause)
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, or menopause
- Underlying health conditions such as diabetes, cancer, HIV, or immune deficiencies
- Oral medications, including anticonvulsants and anti-angina drugs
- Lifestyle habits like smoking
- Poor oral hygiene
- Documented family history of dental disease

What Are the Symptoms of Periodontal Disease?
Symptoms of periodontal disease include bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, a bad taste in the mouth, swollen or tender gums, receding gum line, or teeth that begin to come loose or start to shift.
What People Say About Us!
Gental Dental has great dentist and dental staff. They are very friendly and helpful . They make you feel comfortable and understand your concerns. The staff will work with you no matter your financial situation might be. I highly recommend this dental office.
Click here to read more reviews.
The Stages of Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease develops gradually. It doesn’t suddenly appear overnight as a severe infection involving the tooth root, known as a perio-endo lesion. Gum disease shows its hand all along the path from gum irritation up to tooth loss. You can break gum disease into different types or stages depending on how it has progressed.
- Gingivitis: This is an early gum disease. Basically, it simply means that plaque is beginning to irritate the gums, making them red and prone to bleeding.
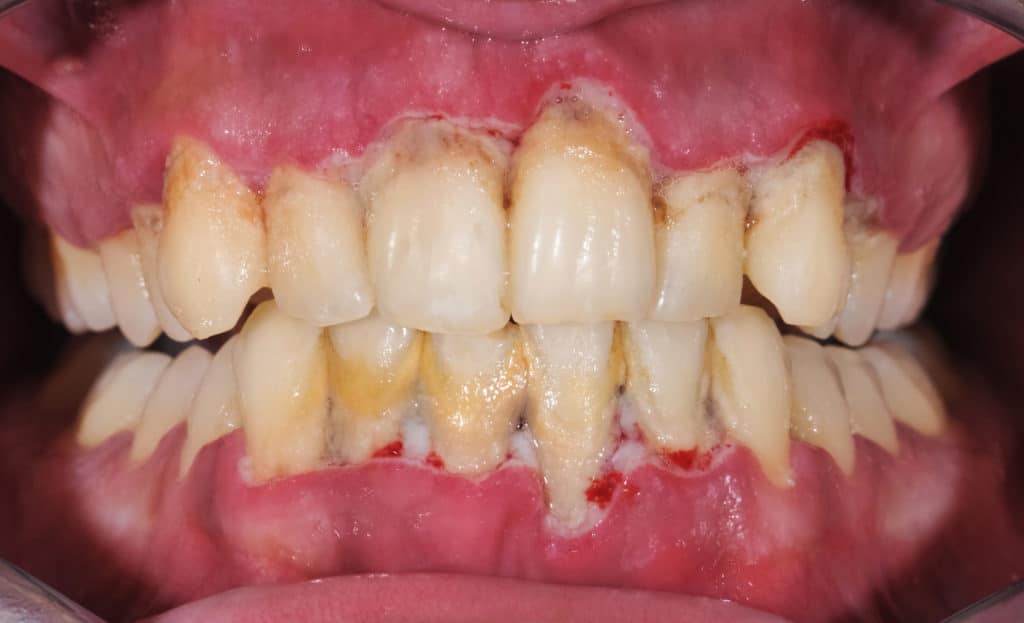
- Chronic periodontitis: Gums have pulled away from the teeth and formed pockets where bacteria are accumulating. Periodontitis always starts with gingivitis. Now the bacteria will begin attacking the bone and tissues attaching the teeth to the jawbone.
- Periodontal abscess: This happens when a pocket forms and becomes infected to the degree that an abscess forms. This will lead to the quick destruction of the attaching tissues of the teeth in the area.
- Perio-endo lesion: This occurs when the infection begins in the tooth root. When decay enters a tooth, if not removed, it can eventually impact the pulp and the nerves and blood vessels within the pulp. This infection moves from the tooth into the surrounding gums.
- Gingival recession: This isn’t always due to plaque buildup. Overly aggressive tooth brushing can also cause this recession. The gums recede, exposing the tooth root that is normally covered by the gums.
Am I at Risk for Developing Periodontal Disease?
People are not predisposed to develop periodontal disease. In almost all cases, it is simply due to poor oral hygiene at home, coupled with the lack of twice-yearly professional cleanings and exams with the team at Gentle Dental.
Smoking and chewing tobacco can increase your chances. Some medications have a side effect that causes dry mouth, which limits saliva production and can make it harder to keep your gums clean. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause can make your gums more sensitive.
Generally, though, this is one disease that is mostly self-inflicted.
How to Prevent Periodontal Disease
Periodontal diseases can be successfully prevented if you practice proper plaque control by:
- Going to the dentist’s office for a professional cleaning appointment at least twice a year.
- Brushing your teeth regularly to remove plaque from the accessible surfaces of the teeth.
- Flossing to eliminate food that has become stuck between the teeth or under the gum line.
Is Gum Disease Reversible?
Gum disease can almost always be reversed. It’s a matter of reducing the pockets, removing the infection, restoring the bone (if necessary), and getting the gums to reattach to the teeth. Of course, how far the gum disease has progressed can dictate whether the reversal is possible.
For instance, if a person has allowed the disease to progress to the point where all of his or her teeth are affected and cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary, and the teeth replaced by dentures or dental implants.
How to Treat Gum Disease
Treatment options for the management of gum disease depend on what stage the disease is in, your overall oral health, and your response to previous treatment.
Nonsurgical treatment options include professional dental cleaning or scaling and root planing, which is a deep cleaning procedure. Both methods remove plaque and tartar buildup from above and below the gum line.
Surgical treatments for periodontal diseases include flap surgery, bone grafting, soft tissue grafting, guided tissue regeneration, and bone surgery.
Surgical options are usually used when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth becomes unhealthy and the disease cannot be corrected using nonsurgical options.
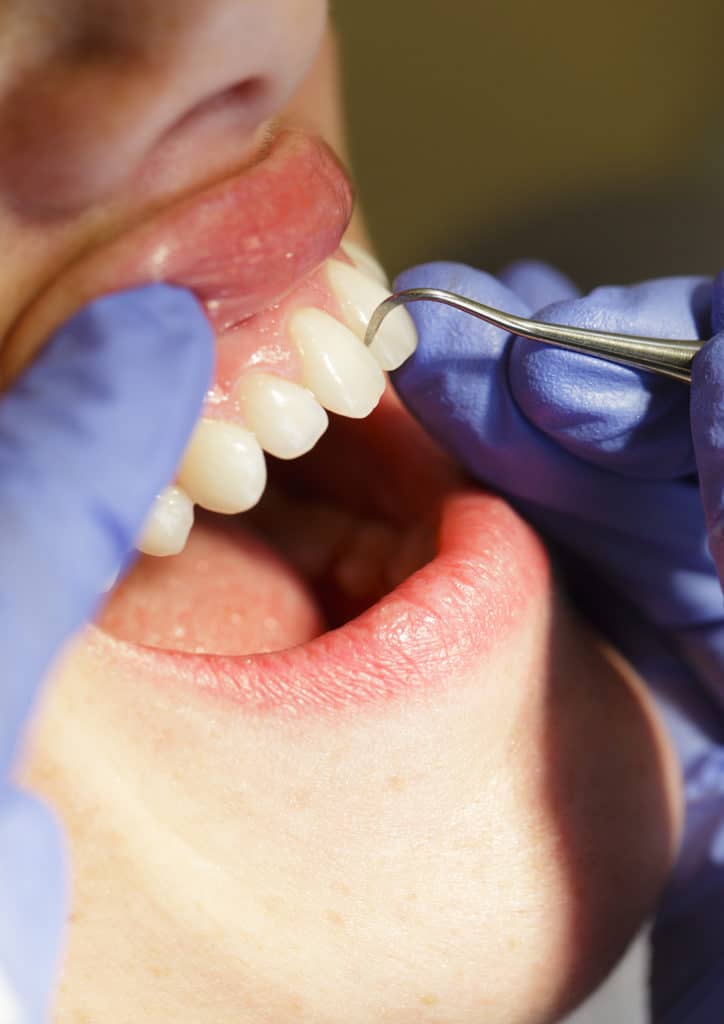
What Kind of Post-Treatment Care Is Necessary?
That depends on the procedures we had to perform. For instance, if we performed root scaling and planing, this is a relatively simple procedure where we remove tartar and plaque from under your gum line and then smooth the surface to help the gums attach back to the root surface. This doesn’t require any post-treatment care, other than better home hygiene moving forward.
Other more involved procedures, such as soft tissue grafting or flap surgery, involve more attentive care during recovery to be sure to keep the infection from recurring.
We’ll explain what you need to do in detail after our periodontal disease treatments.
Is the Treatment of Gum Disease Permanent?
Yes, these treatments performed by our Gentle Dental team to stem and reverse your periodontal disease are permanent treatments, meaning your results will last and your gum disease will be gone.
But this depends on your actions. Remember, it’s poor home hygiene and a lack of professional cleanings and exams that allowed the gum disease to develop in the first place. It’s going to take a new dedication to excellent home hygiene moving forward. Otherwise, gum disease can return.
What Happens if I Don’t Have My Gum Disease Treated?
Gum disease develops gradually, often starting with plaque buildup. The bacteria in plaque release acids that irritate the gums, leading to gingivitis. Without treatment, plaque can harden into tartar, which builds up along and beneath the gumline, advancing the condition into more serious stages of gum disease.
As tartar collects, the gums may start to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria thrive. Over time, this infection can damage the gums, the tissues connecting your teeth to your jawbone, and the tooth roots. Eventually, teeth may loosen, decay, or require removal.
If gum disease is left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss, bone deterioration, and increase the risk of other health complications, such as heart disease. Early care and consistent hygiene are the best ways to protect your oral health.
Patient Testimonial
What Are Scaling and Root Planing?
Scaling and root planing are deep-cleaning treatments used to manage gum disease. This procedure goes beyond a regular dental cleaning by removing built-up plaque and tartar from both the teeth and the roots below the gumline.
During the treatment, your dentist will numb the area with a local anesthetic to keep you comfortable. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from above and below your gums. Root planing then smooths out the rough surfaces of your tooth roots. This step is important because rough roots make it harder for your gums to heal and reattach properly.
If you have gum pockets in more than one area of your mouth, your deep cleaning will likely be done in stages, treating one section at a time to allow for proper healing. This process helps stop the progression of gum disease and encourages healthier gums.
Is Scaling and Root Planing Effective?
Scaling and root planing are the gold standard of nonsurgical gum disease treatments. Keep in mind that it cannot reverse severe periodontal disease. However, if your gum infection is limited to the gingiva and the roots of some teeth, yet your jawbone and periodontal ligament remain in good condition, this service can significantly improve your oral health.
The long-term results of scaling and root planing will be better if you don't smoke and do not have diabetes. That said, you can sustain relatively good oral health after this treatment if you take impeccable care of your teeth and take measures to manage your lifestyle and general health.
What Surgical Treatments Are Used to Treat Gum Disease?
If your gum disease has severely damaged your periodontal tissue or jawbone, there is a risk that you could lose one or more teeth in the affected area. Several surgical procedures may be considered as we seek to preserve your teeth and prevent further damage. These include:
- Flap Surgery: This is done to reduce periodontal pockets. To do this, the doctor makes tiny cuts in the gums before performing scaling and root planing.
- Soft Tissue Grafting: Done to correct gum recession, soft tissue grafting attaches tissue taken from the roof of your mouth to the damaged area.
- Bone Grafting: Performed to rebuild bone tissue where severe damage has occurred, this procedure places natural or synthetic bone material into the jaw, where it integrates over time.
- Tissue Regeneration Treatment: The placement of biocompatible material may be done to close gaps between teeth and bone. This helps promote the growth of new bone cells.
- Tissue-Stimulating Proteins: These may be applied to an area of infection around the root of a tooth to help regrow healthy tissue.
How Smoking or Diabetes Impacts Gum Disease Progression
Smoking and diabetes both make it harder for your gums to stay healthy and fight infection. Smoking weakens your body’s ability to heal, which means gum tissue damaged by bacteria takes longer to recover. Tobacco use also reduces blood flow to the gums, limiting oxygen and nutrients needed for healing. As a result, smokers are more likely to develop gum disease, and treatment tends to be less successful.
Diabetes, especially when not well-controlled, affects your body’s immune response. High blood sugar levels can increase inflammation and slow healing, making it easier for bacteria to damage gum tissue. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gum disease and may have more severe infections that progress faster.
Both smoking and diabetes not only raise your risk of developing gum disease but also make it harder to manage and treat once it begins.
How Gum Disease Can Affect Your Overall Health
Gum disease can impact your health beyond your mouth. Research has shown a clear link between periodontal disease and conditions like heart disease. When bacteria from gum infections enter your bloodstream, they can trigger inflammation in other areas of your body.
This inflammation may contribute to the buildup of plaque in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Gum disease has also been connected to other health concerns such as diabetes complications, respiratory disease, and certain pregnancy issues like low birth weight.
Taking care of your gums through regular dental visits and good home care can support not just your oral health but your general well-being as well.
Why Choose Gentle Dental Care?
Schedule Your Consultation
If you are dealing with periodontal disease in Edison, Piscataway Township, New Brunswick, Metuchen, or Woodbridge Township, NJ, call 732-549-5660 to schedule your visit. You can also stop by our office or fill out our online contact form to get started.